IMS AKA Session Registration Message Flows
IMS AKA Registration services include:
Registration of a new IMS AKA session
A successful IMS AKA Registration is accomplished by two SIP Register request messages sent to the subscriber's S-CSCF and two SIP Register response messages to the requesting subscriber. Information neccesary to perform an authentication and set up the two IPsec channels are provided in the SIP message headers. Some of the SIP message headers are specific for IMS.
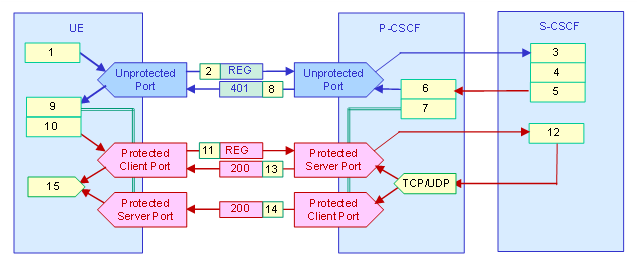
Figure F-27: >Message flow for Initial Registration (UDP or TCP).
The following list explains simplified the procedures for Initial Registration in the figure above.
-
The UE builds an unauthenticated SIP Register request message.
-
The SIP Register request message is sent to the P-CSCF’s unprotected server port.
-
The SIP Register request message is passed to the UE’s home S-CSCF where the UE’s SIP identity is validated.
-
The S-CSCF obtains the requesting subscriber's security information from the HSS.
-
The S-CSCF sends a SIP 401 Authentication Required response message to the P-CSCF.
The message contains encryption keys to be used by IPsec on the P-CSCF side.
The message also contains authentication information to the UE. -
A modified SIP 401 response message is built by the P-CSCF without encryption keys but with a Security-Server header with IPsec information.
-
The P-CSCF prepares the IPsec channels to enable reception of the authenticated SIP Register message.
-
The modified SIP 401 response message is sent to the UE’s unprotected client port.
-
The S-CSCF is authenticated by the UE and the encryption keys for the IPsec channels are calculated.
The UE creates the IPsec channels and configures the related Security Associations. -
The UE builds an authenticated SIP Register request message.
-
The UE sends the SIP Register request message to the P-CSCF’s protected server port.
-
The SIP Register request message is passed to the S-CSCF where the UE is authenticated.
A session is created and the HSS is updated. A SIP 200 OK response message is returned to the UE. -
The SIP 200 OK response message is sent to the UE’s protected client port if the TCP protocol is used.
-
The SIP 200 OK response message is sent to the UE’s protected server port if the UDP protocol is used.
-
The session is created.
Re-Registration of an IMS AKA session
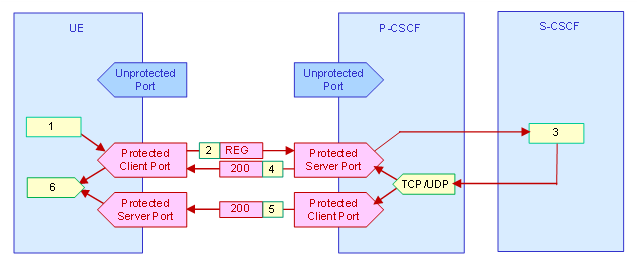
Figure F-28: Message flow for Re-Registration (UDP or TCP).
The following list explains simplified the procedures for Re-Registration in the figure above. NB. This Re-Registration does not entail allocating a new channel pair. If new channels have to be allocated, double channel pairs will have to be kept for a time-out period, until all messages using the old channels have been handled.
-
The UE builds a SIP Register request message with authentication header and Expire time header time.
-
The SIP Register request message is sent to the P-CSCF’s protected server port.
-
The Re-Register request message is sent to the subscribers home S-CSCF.
The S-CSCF extendeds the UE’s session and a new expire time is set.
A SIP 200 OK response message with a new Expire time is returned to the UE. -
The SIP 200 response message is sent to the UE’s protected client port if the TCP protocol is used.
-
The SIP 200 response message is sent to the UE’s protected server port if the UDP protocol is used.
-
The UE updates the session expire time.
Re-Registration may include switch to new secure channels (not shown here).
De-Registration of an IMS AKA session.
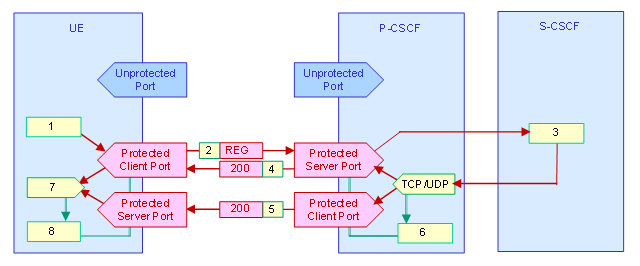
Figure F-29: Message flow for De-Registration during an ongoing session (UDP or TCP)
The following list explains simplified the procedures for De-Registration in the figure above.
-
The UE builds a SIP Register request message with authentication header and Expire time set to zero.
-
The SIP Register request message is sent to the P-CSCF’s protected server port.
-
The De-Register request message is passed to the subscribers home S-CSCF.
The S-CSCF closes the UE’s session.
The HSS is updated about the closed session.
A SIP 200 OK message is returned to the UE. -
The message is sent to the UE’s protected client port if the TCP protocol is used.
-
The message is sent to the UE’s protected server port if the UDP protocol is used.
-
The P-CSCF removes the Security Associations and closes the IPsec channels.
-
The UE closes the session.
-
The UE removes the Security Associations and closes the IPsec channels.

